DNA test assesses breast cancer ‘risk score’
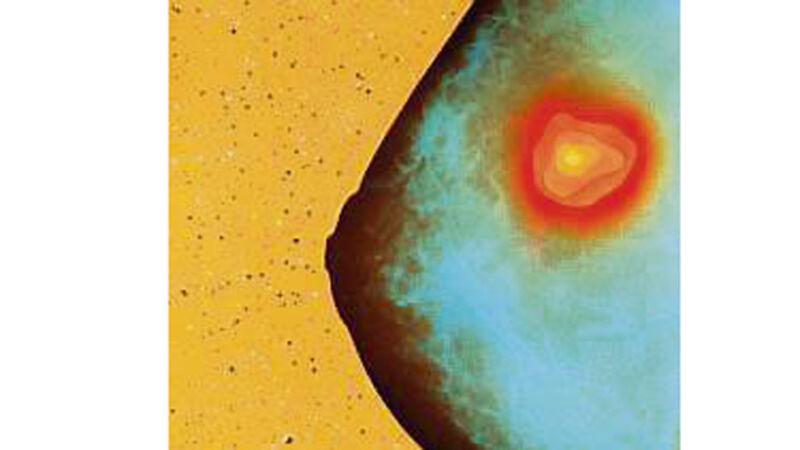
Researchers said that improving the accuracy of risk analysis using genetic screening could help breast cancer prevention and save lives.
Professor Douglas Easton, director of the Centre for Cancer Genetic Epidemiology at the University of Cambridge, who co-led the study, said he hoped genetic risk prediction will become part of routine breast screening in future.














