Companies gearing up for 5G era of industry digitisation

The roll-out of 5G will bring more economic benefits in manufacturing than in any other industry.
In this digital era, Information Communication and Technology (ICT) is the leading industry.
We are advancing ‘at light speed’ with new technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), Microservices and many more.
With these advancements there is a necessity for the ICT sector to realign their business plans and reform themselves to keep up. This is how the focus of business technology has shifted to 5G.

5G is expected to serve as the ‘Catalyst’ that gives rise to better business and societal opportunities through digitization. According to HIS “5G is superior to anything out there currently, it is expected to revolutionise the industrial landscape and facilitate in unlocking global economic output of up to USD$12.3 trillion in 2035.
Manufacturing is expected to have the largest share of 5G enabled economic activity in 2035, up to USD$3.4 trillion” The set of technologies behind this latest standard will make 5G the disruptive generation, which will utterly transform the economy.
Firstly, 5G will boost capacity massively. It will take us into the era of ultra-high-speed, with data transmission speeds potentially 10 times or even 100 times faster than 4G. Secondly, 5G will be disruptive due to its extremely low latency, which means at less than a millisecond, we are almost at real-time.
Lastly, the extensive network coverage of 5G will provide connectivity everywhere and support up to 1 million devices per square kilometre connected simultaneously. This extraordinary boom in connectivity will make it possible to develop the Internet of Things (IoT) and industrial uses of artificial intelligence (AI) at scale. For example, 5G combined with AI and IoT clears the route for connected and autonomous vehicles.
It could enable a plethora of features such as collision avoidance, real-time traffic routing, pedestrian’s safety alerts, emergency braking etc. Although several features of connected vehicles have been tested and partially implemented in developed nations over LTE, the power of this connected vehicle ecosystem can truly be harnessed through the introduction of 5G.
For Smart Cities, there will be considerably more ways to manage the community life in near real-time like enhanced security and mobility, measure pollution, optimise energy consumption, improve waste management, etc. The list is virtually endless.
Although existing 4G networks have already been deployed in smart cities around the world, they are limited by the number of connections they can support, the data they can transmit, and most importantly the speed they can offer, all of which create hurdles in deployment of smart cities use cases. 5G is expected to overcome these hurdles, and allow large number of connections, providing super-high bandwidth, and ultra-low latency based communications, to build a connected city – a smarter city.
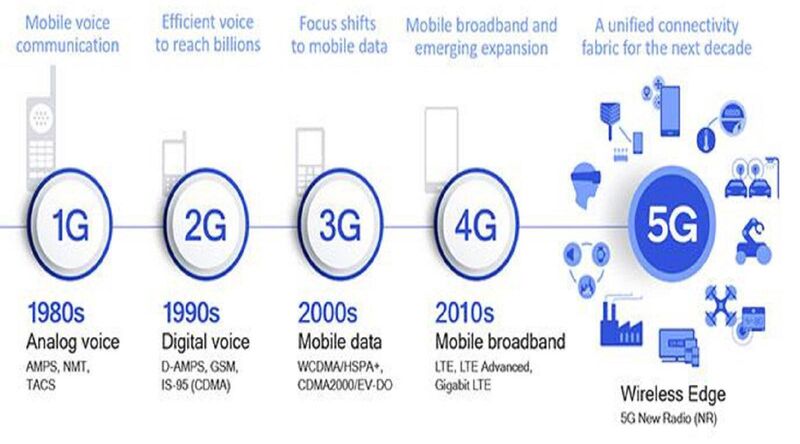
5G will provide the infrastructure to roll out these innovations that appear promising today. Therefore, 5G opens up a whole world of new possibilities. Until the fourth generation network (4G), consumers were the first to benefit from each new generation of wireless technology. However, the main interest of 5G lies in business-to-business markets. This next generation of mobile telecommunications will become the backbone of industrial operations in the broadest sense.
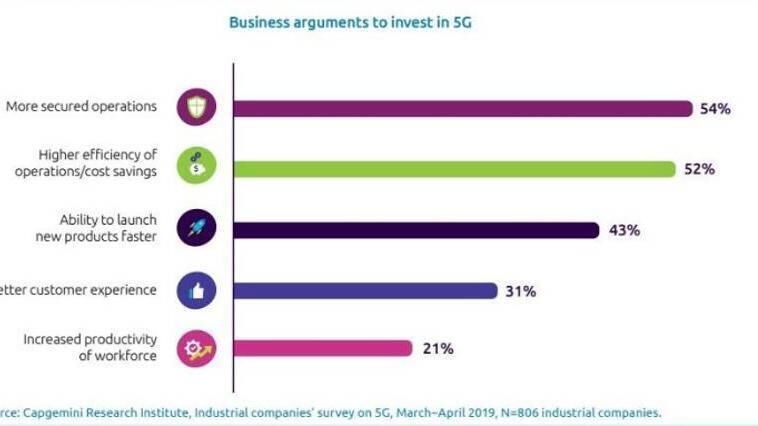
According to the latest findings from the Capgemini Research Institute, “5G technology is critical for a digital transformation strategy….due to its versatility, flexibility, and reliability.”
The roll-out of 5G will bring more economic benefits in manufacturing than in any other industry. It will help to streamline operations which in turn will improve the business output. The digital transformation of the manufacturing industry is already in the initial stages, widely known as Industry 4.0.
5G is a decisive leap towards the automation of industrial processes, and eventually towards autonomous industrial processes. We are about to replace outdated industrial technologies based on dedicated, closed and costly systems with the industrial IoT.
In other words, connected machines controlled and supervised from a distance in real-time, with two-way data communications that no longer depend on wired networks. Hence, making the manufacturing processes smart, intelligent and dynamic, which can lead to improvements in functions such as supply chain logistics, inventory management, product development etc.
- It will make it easier to adapt to the changing demands of the production cycles, to move to shorter production runs and offer more customization and personalization;
- It will increase the productivity and ensure better quality control:
- Constant gathering of data to anticipate problems on production lines and prevent them from happening.
Smart manufacturing, a subset of Industry 4.0 is defined by The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) as being “fully-integrated, collaborative manufacturing systems that respond in real-time to meet changing demands and conditions in the factory, in the supply network, and in customer needs [4].”
With anything, there will be a set of risks associated with all these new opportunities. Evidently, the biggest risk is the vulnerability of interconnected systems. The large-scale integration of devices, some of them with inadequate security could be exploited. Another major risk is that businesses of all sizes could fail to seize all the opportunities that 5G has to offer (hard to imagine at this stage) and lose out to competitors that could adapt more quickly.
The digital transformation of businesses i.e. their capacity to use Artificial Intelligence, leverage their data and embrace IoT will depend on their ability to convert to 5G technologies. But they need to adapt their value propositions and solutions to offer new services, and take into consideration the notions of security. Businesses will need to rely on trusted 3rd parties who understand the technologies and the limitations associated with critical environments. This is key to their ability to guarantee cybersecurity and it's a crucial requirement for developing and rolling out 5G across any industry or any ecosystem.
A collective effort from industrial companies and research centres is required to exploit the potential 5G has for digital transformation. The areas where 5G can add value, both in the immediate and longer term need to be identified and the right implementation of road map to be completed. By working closely with institutes like The Nimbus Research Centre, businesses can avail of the full potential of this transformative technology.









