Back in the ozone: How we plugged the hole in the sky
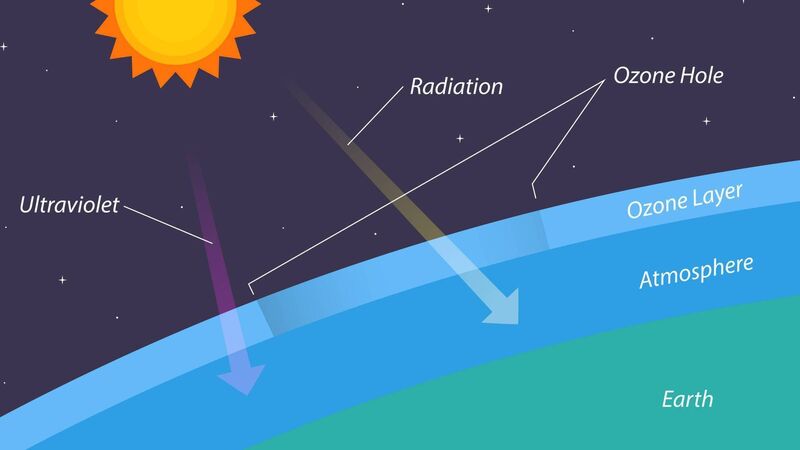
The Earth’s ozone layer is the invisible shield that protects us from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays.
Once upon a time, well in the 1980s, the world looked up and discovered we’d poked a hole in the sky. Not metaphorically, not in some sci-fi dystopia, but literally, a yawning gap in Earth’s ozone layer — the invisible shield that protects us from the Sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. And the culprit wasn’t alien invaders or a rogue comet, but something far more mundane: hairspray, fridges, and air-conditioners.
The hole over Antarctica quickly became a potent symbol of human overreach. Scientists had been warning since the 1970s that chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), the miracle chemicals that made spray-on deodorant, whipped cream in a can, and frost-free freezers possible, could destroy ozone molecules in the upper atmosphere. But it wasn’t until 1985, when British scientists Joe Farman, Brian Gardiner, and Jonathan Shanklin published shocking measurements from Antarctica that it was fully apparent. The data showed a massive seasonal depletion of ozone each spring.








