Sleep deprivation effects drivers in a similar way to drinking alcohol
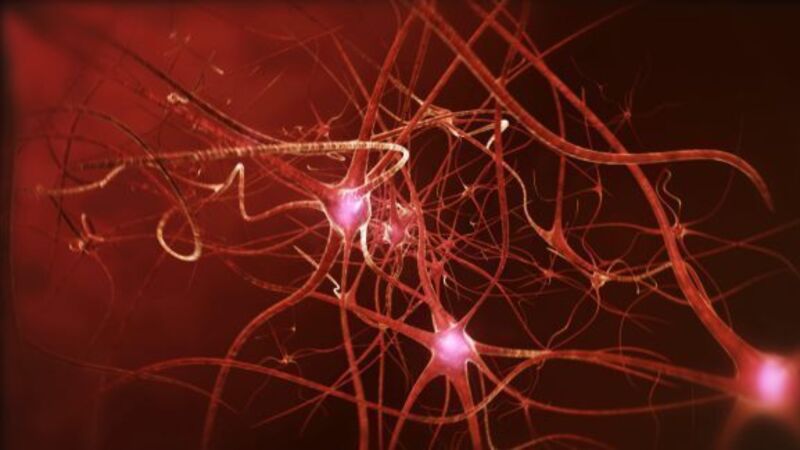
Sleep deprivation disrupts brain cell communication in much the same way as alcohol, research has shown.
Exhausted neurons respond more slowly than usual and take longer to transmit weaker signals, a study found.














